AI is becoming a key part of remote care. It helps clinics monitor patients, spot risks early, and act fast when health readings change. But with these benefits come real concerns. Clinics must protect patient data, follow clear rules, and use AI in a safe and fair way.
Many doctors say they trust AI more when they understand how it works and how the rules keep patients safe. A recent McKinsey report shows that over 70% of healthcare leaders want stronger AI guidelines before using these tools at scale. This shows that ethics and compliance are no longer “optional.” They are central to how remote care works in 2026.
This blog explains how to navigate the ethical and regulatory landscape of AI in remote care. You will learn the key rules, common risks, best practices, and how clinics can use AI with confidence.
What Does “Navigating the Ethical and Regulatory Landscape of AI in Remote Care” Mean?
Navigating this landscape means understanding the rules, risks, and responsibilities that come with using AI in patient care. It also means making sure your clinic uses AI in a safe, fair, and transparent way. When clinics follow the right steps, AI becomes a tool that supports doctors rather than creating new problems.
In simple terms, it means:
- Knowing the laws that guide AI in healthcare
- Protecting patient data
- Keeping humans in control of clinical decisions
- Making sure AI alerts are clear, accurate, and unbiased
- Reviewing AI tools to confirm they meet ethical and regulatory standards
Key Ethical Challenges in AI for Remote Care
AI brings many benefits to remote care, but it also comes with real challenges. Clinics must understand these risks to use AI safely. The table below explains the main issues, what they mean, and why they matter.
| Challenge | What It Means | Why It Matters |
| Bias in AI results | AI may give unfair alerts if trained on unequal data. | Biased alerts can harm patient trust and lead to wrong decisions. |
| Over-reliance on automation | Staff may depend on AI more than clinical judgment. | Clinics must keep “human-in-the-loop” to avoid missed risks. |
| Alert fatigue | Too many alerts can overwhelm staff. | Important warnings may be ignored or missed. |
| Lack of transparency | AI tools may not explain why an alert was generated. | Doctors need clear, simple reasoning to act on alerts. |
| Data privacy risks | Patient data may be exposed if the system is weak. | HIPAA requires strong protection, or clinics face fines. |
| Misinterpretation of trends | AI may spot patterns that are not clinically meaningful. | False trends can cause unnecessary follow-ups or stress. |
| Poor validation | Tools may not be tested well across diverse patients. | FDA expects safe, validated models to protect patients. |
Regulations That Shape AI in Remote Care (U.S. Focus, 2026 Update)
AI in remote care is not fully regulated by one single rule. Instead, clinics must follow a mix of guidelines from different U.S. agencies. These rules help protect patient safety, data privacy, and clinical accuracy. Understanding them is key to using AI the right way.
Below is a simple review of the main regulations that guide AI in remote care today.
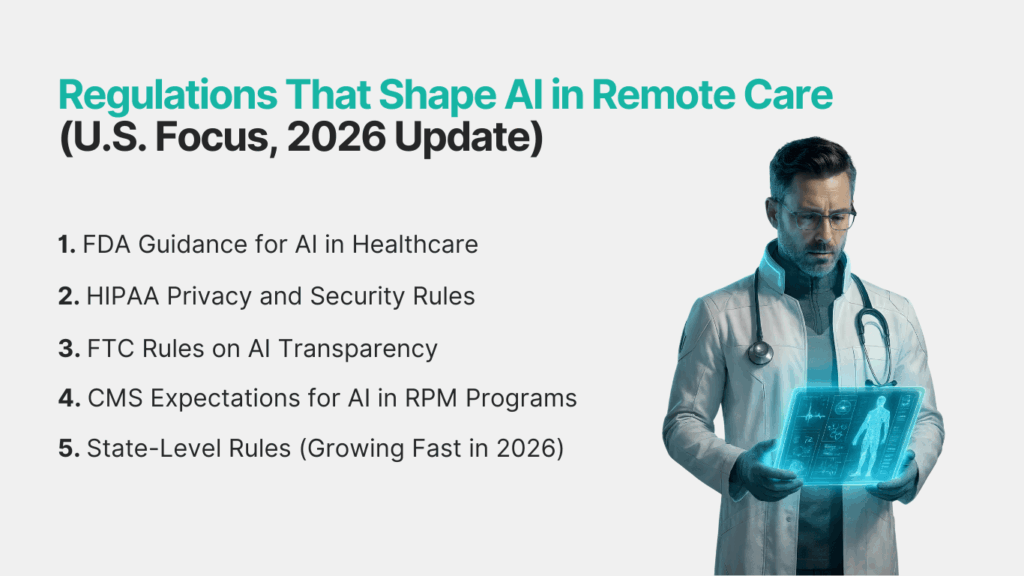
1. FDA Guidance for AI in Healthcare
The FDA reviews many AI tools used for clinical decisions. They focus on:
- Safety
- Accuracy
- Clear explanations for doctors
- Human oversight requirements
If AI affects diagnosis, alerts, or risk scores, it may fall under FDA review.
2. HIPAA Privacy and Security Rules
HIPAA does not change for AI. AI systems must follow the same rules as any other health tool. This includes protecting PHI, encryption in storage and transit, access control, audit logs and no training AI models on patient data without consent. In 2026, HIPAA enforcement has become stricter due to rising digital health breaches.
3. FTC Rules on AI Transparency
The FTC requires companies to be honest about:
- How AI works
- What data it uses
- What it does not do
- Any risks patients should know
If a clinic uses AI to monitor patients, the FTC expects clear, simple disclosure.
3. CMS Expectations for AI in RPM Programs
CMS does not approve or reject AI tools. But CMS expects clinics to:
- Keep human oversight
- Follow HIPAA
- Document workflows
- Show that AI alerts support—not replace—clinical judgment
- Maintain clear clinical notes
If AI insights affect RPM billing, CMS expects proper documentation.
4. State-Level Rules (Growing Fast in 2026)
Some states have added extra requirements. Examples:
- Texas: strong data privacy laws for digital health tools
- California: rules on automated decision-making and consent
- Colorado: transparency rules for AI-driven health tools
Clinics must check their state guidelines before using AI in care workflows.
The Role of HIPAA in AI-Driven Remote Care
HIPAA plays a major role in how AI is used in remote care. Even though AI is new, the rules stay the same: patient data must be kept safe at all times. Any AI tool that deals with PHI must follow HIPAA privacy and security standards, just like any other digital health system.
Below is a simple breakdown of how HIPAA affects AI-powered remote care.
Key HIPAA Rules Clinics Must Follow
- Protect all patient data (PHI)
AI systems must not expose, misuse, or wrongly store patient information. - Use encryption
Data must be encrypted when stored and when shared. - Control who can access data
Only approved staff should view PHI used in AI workflows. - Audit logs
Clinics must keep track of who accessed patient data and why. - Secure storage
Data must be stored in HIPAA-compliant servers. - Business Associate Agreements (BAA)
Vendors offering AI tools must sign a BAA with clinics. - Training data rules
Clinics must not use real patient data to “train” or “improve” AI models without proper consent.
Do and Don’t List for AI Under HIPAA
| Do | Don’t |
| Use AI tools with a signed BAA | Upload PHI into AI tools with no compliant storage |
| Inform patients how AI works | Train AI models on PHI without consent |
| Keep humans in the loop | Let AI make final decisions |
| Review security settings often | Ignore audit logs or access reports |
HIPAA does not block clinics from using AI. It only ensures they use AI responsibly, safely, and with full patient protection.
How Clinics Can Use AI Safely in Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
AI can help clinics work faster and catch risks early, but it must be used with control and care. Safe use means combining AI insights with human judgment, clear workflows, and strong documentation. Below is a simple step-by-step guide for safe AI use in RPM.
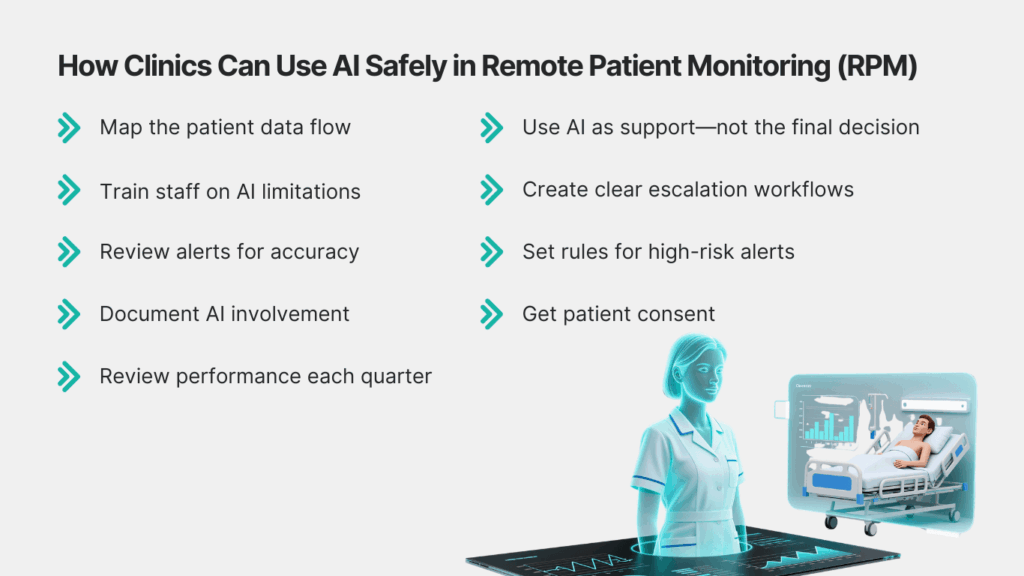
Step-by-Step: Safe Use of AI in RPM
- Map the patient data flow
Know what data goes into the AI tool, how it is processed, and where it is stored. - Use AI as support—not the final decision
Doctors must review alerts, trends, and suggestions before acting. - Train staff on AI limitations
Make sure all team members understand what AI can and cannot do. - Create clear escalation workflows
Every alert should have a set path: AI flag → nurse review → doctor review → action. - Review alerts for accuracy
Check if AI insights match real clinical outcomes. - Set rules for high-risk alerts
For example:- Auto-flag BP spikes
- Send instant notifications for critical thresholds
- Document AI involvement
CMS expects clinics to show how AI insights supported RPM reviews. - Get patient consent
Patients must know that their readings may be analyzed by AI tools. - Review performance each quarter
Check false alerts, missed alerts, and overall trends.
Best Practices to Reduce AI Risks in Remote Care
AI becomes safer when clinics follow clear daily practices. These steps help reduce errors, protect patients, and keep care teams in control. They also help clinics stay aligned with HIPAA, CMS, and FDA expectations.
Below is a simple list of proven best practices.
Best Practices Clinics Should Follow
- Keep humans in the loop
AI can support decisions, but doctors must approve final actions. - Use AI tools with clear explanations
Avoid “black box” tools that do not show how alerts are generated. - Review alerts regularly
Check for false alarms, missed alerts, or unusual patterns. - Limit access to patient data
Only trained staff should view PHI linked to AI tools. - Use validated devices and models
Tools should be tested across different age groups, conditions, and backgrounds. - Give patients simple transparency
Tell them how their data is used and what AI does. - Update consent forms
Keep consent easy to read and aligned with your state’s AI rules. - Track high-risk patients separately
AI can support risk scoring, but nurses and doctors should add manual review notes.
Future Trends: Where AI and Remote Care Are Heading in 2026
AI in remote care is moving fast. In 2026, clinics will see tools that are safer, more accurate, and easier to use. Below are the top trends shaping AI in remote care this year.
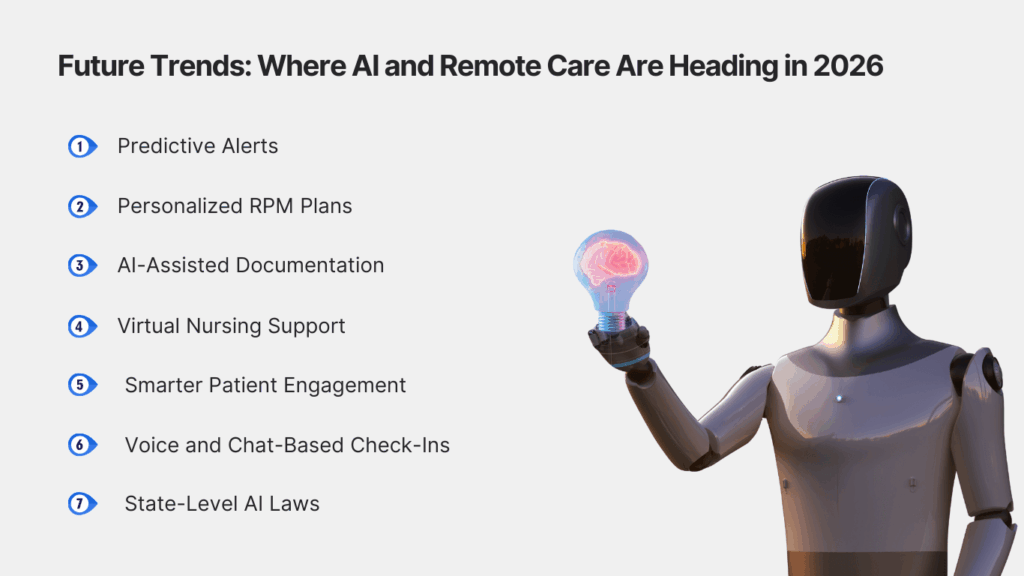
1. Predictive Alerts
AI will start showing early warnings before readings become risky. Example: spotting signs of rising blood pressure days before a spike.
2. Personalized RPM Plans
AI will help create care plans based on each patient’s habits, patterns, and history. This makes remote care more tailored and effective.
3. AI-Assisted Documentation
Tools will help auto-fill notes for RPM reviews. Doctors will still approve everything, but the workload becomes lighter.
4. Virtual Nursing Support
AI will assist nurses by sorting alerts, flagging urgent cases, and guiding next steps. This helps clinics manage more patients without adding extra staff.
5. Smarter Patient Engagement
AI will help identify which patients need reminders, coaching, or check-ins. This supports better compliance and better outcomes.
6. Voice and Chat-Based Check-Ins
Patients may give daily updates through voice or chat systems. AI helps organize the input while the care team reviews final decisions.
7. State-Level AI Laws
More states will pass rules on how AI should be used in healthcare. Clinics will need tools that stay updated with changing requirements.
Use AI in Remote Care With Safety, Clarity, and Confidence
AI can make remote care faster, safer, and more reliable—when it’s used the right way. With clear rules, strong ethics, and human oversight, clinics can get real value from AI without risking patient trust or breaking compliance standards.
If your clinic wants to use AI-supported RPM without worrying about privacy, audits, or unclear alert logic, CandiHealth is built for you. Our platform offers:
- HIPAA-compliant data protection
- AI-assisted alerts with full transparency
- Clear documentation for CMS billing
- Simple onboarding for clinics and patients
You stay in control. We handle the tech, the compliance, and the heavy lifting. See how CandiHealth helps your clinic deliver safe, ethical, and compliant remote care—book a quick walkthrough today.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is AI safe to use in remote patient monitoring?
Yes. AI is safe to use in remote patient monitoring when clinics follow HIPAA rules, keep humans in control, and review all alerts before taking action. AI can flag risks early and track trends, but final decisions must come from certified clinicians. With the right safeguards, AI helps improve patient care without replacing doctors.
How is AI used in remote patient monitoring?
AI helps clinics track patient readings, spot early risks, and find health trends. It supports doctors by organizing data and sending smart alerts, but humans still make all final care decisions.
Is AI allowed under HIPAA for remote care?
Yes. HIPAA allows AI in healthcare as long as patient data is protected. The AI system must use encryption, secure storage, access control, and a signed BAA. Clinics must make sure no PHI is used to train AI without consent.
What ethical issues come with using AI in healthcare?
The main issues include bias, alert errors, unclear explanations, privacy concerns, and over-reliance on automation. Clinics must keep humans involved and regularly review AI alerts to stay safe and compliant.
Does AI replace doctors in remote care?
No. AI does not replace doctors. It only supports them by showing patterns, highlighting risks, and sending alerts. All clinical decisions—diagnosis, medication, follow-up—must come from certified clinicians.
What should clinics check before using an AI tool for RPM?
Clinics should check:
- HIPAA compliance
- Clear alert logic
- Vendor BAA
- Data storage security
- Human-in-the-loop workflows
- Accuracy and validation reports
- Easy consent for patients